Abstract: The waste paper papermaking wastewater was treated by pre-oxidation coagulation method. Studies have shown that with KMnO4 as the oxidant under the optimal treatment conditions, the CODCr removal rate of wastewater reaches 89% to 94%, and the removal rate of BOD5 reaches 90%.
Keywords: pre-oxidation KMnO4 waste paper papermaking wastewater
Foreword
 With the increasing tension in papermaking resources and the continuous improvement of people’s environmental awareness, the recycling of waste paper has attracted more and more attention. Waste paper has become one of the main raw materials for paper production. Although waste paper does not produce "black liquor" in the papermaking process, there is still a large amount of waste water containing contaminants such as fine fibers, inks, resins, pigments, chemicals, and mechanical impurities. This waste water will be directly discharged without treatment and will cause pollution and harm to the environment.
Waste paper papermaking wastewater mainly comes from the pulping part of the washing wastewater. According to the difference between the waste paper source and the production process, the characteristics of the washing wastewater are different. The waste water contaminant content of a waste paper mill in this paper is roughly: CODCr 500-1000mg/L, BOD5 200-450mg/L, SS 500- 800mg/L, color 250 ~ 600 times, pH 6.5 ~ 7.3, appearance was dark gray. The amount of washing wastewater is 150 to 200 m3/t.
 Waste paper papermaking wastewater treatment technology currently used in China is coagulation sedimentation (or air floatation). With the application of new organic and inorganic polymer flocculants, the coagulation and sedimentation method can not only effectively remove the SS and color in the wastewater, but also remove most of the COD.
 The author used flocculation precipitation method to study the aforementioned wastewater and obtained the best treatment conditions. The treated wastewater basically contains no suspended matter, the color removal rate is above 98%, the CODCr removal rate is between 70% and 75%, and the BOD5 removal rate is between 60% and 70%. As the treated water quality has become clear and transparent, the idea of ​​using the treated clean water for washing the pulp has been proposed to achieve the goal of reducing the total amount of waste water discharged and saving production water [1]. In order to avoid the impact on the pulp washing process due to the high COD content in the reuse water and the accumulation of COD, and in order to improve the quality of the discharged water, it is necessary to explore more effective waste paper papermaking wastewater treatment technologies.
In the field of wastewater treatment, chemical oxidation has received more and more attention [2–4]. The author used KMnO4 pre-oxidation method to study the waste paper papermaking wastewater treatment process. 
1 Test
  1.1 Water samples
The test sample was taken from a paper mill. The factory mainly uses imported waste paper (pictures, books, newspapers, etc.) as raw materials to produce toilet paper, cardboard and kraft paper. Its papermaking wastewater (ie, "white water") is treated by air flotation and recycled, and other wastewater is collected and discharged into a discharge ditch. The test sample was taken from the drain.
  1.2 Major pharmaceutical agents and instruments
 Instruments: stepless speed regulated stirrer, pH-25 pH meter, 722 spectrophotometer, HH-5 chemical oxygen consumption analyzer, etc.
Pharmacology: Potassium permanganate, sodium hypochlorite, hydrogen peroxide, ferrous sulfate, polyacrylamide, JA compound coagulant and so on.
  1.3 Wastewater treatment process
 Chemical pre-oxidation-coagulation method. Take 500mL waste water sample in a beaker, add chemical oxidant under stirring, react to the specified time, and then treat according to the optimal process conditions of the coagulation and sedimentation method, then slowly pour it into a 1000 mL measuring cylinder and let it stand for 10 minutes. After the clarification of wastewater analysis related items. 
2 Results and Discussion
In the previous study on coagulation and sedimentation, the removal of suspended solids and color has achieved satisfactory results. Therefore, the purpose of this experiment was to increase the removal rate of COD. The KMnO4, lanthanum NaClO, and Feton reagents (H2O2+Fe2+) were used to perform the conditions test. The KMnO4 pre-oxidation method had the best treatment effect. Therefore, the KMnO4 pre-oxidation process conditions were optimized.
 In order to eliminate the influence of other factors, KMnO4 blanks (the other processing conditions are the same) were tested in each set of tests, and the CODCr removal rate (II) was used as the evaluation basis for each test. The expression of CODCr removal rate (II) is as follows:
      CODCr removal rate (II) = (CODCr (I) - CODCr (II)) / CODCr (I)  
 formula CODCr (â… ) - when KMnO4 blank, the waste water after treatment CODCr remaining;
CODCr (Ⅱ) - When adding KMnO4, the waste water after treatment CODCr remaining.
 Effect of 2.1 KMnO4 dosage on CODCr removal rate
The KMnO4 dosing amount has a greater influence on the CODCr removal rate, which is clearly reflected in the KMnO4 dosing amount-CODCr removal rate (II) curve shown in FIG. Under the condition of 30min oxidation reaction time, when the dosage of KMnO4 is less than 10mg/L, the CODCr removal rate (II) increases gradually with the increase of KMnO4 dosage; when the KMnO4 dosage is greater than 10mg/L, CODCr removal (â…±) with increasing dosage of KMnO4 increase rapidly, and the dosage of 13mg / L reaches peak value; when KMnO4 dosage continues to increase, the removal rate of CODCr in (â…±) slowly decreased. This indicates that the presence of KMnO4 dosage optimum value, this time showing the oxidation, the effectiveness of the most prominent coagulation aid. The optimum dosage of KMnO4 obtained in this experiment was 13 mg/L, and the corresponding CODCr total removal rate was 87.0%.
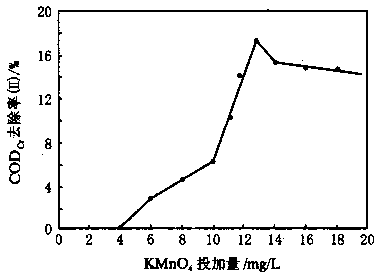
 Figure 1 Relationship between KMnO4 dosage and CODCr removal rate (II) (oxidation reaction time: 30 min; pH: 7.01; wastewater CODCr: 644 mg/L)
 should be noted that KMnO4 blank test obtained CODCr removal rate was still flocculation and sedimentation method CODCr removal rate of about 5%. This is due to the blank test and the addition of oxidant test, there is a certain mixing time before flocculation settled, so that part of the CODCr wastewater contact with the air oxidation or dissolved oxygen in water to flocculate caused by dissolved oxygen. (To be continued)
Dining chair is a common seat in restaurants, bars, cafes and other places for people to use when dining. According to different design styles, materials, functions and uses, dining chairs can be divided into a variety of categories. The following will be a brief introduction to the product classification of dining chairs.
First, according to the design style classification
1. Simple modern style: Simple modern style dining chairs usually use simple lines and Outlines, focusing on functionality and practicality, suitable for modern restaurants and cafes.
2. European classical style: European classical style dining chairs pay attention to gorgeous details and decoration, common hollow carving design and curve shape, suitable for high-end restaurants and banquet places.
3. Nordic style: Nordic style dining chairs focus on simple, natural and comfortable design, usually using wood materials and simple lines, suitable for family restaurants and cafes.
4. Industrial style: Industrial style dining chairs often use metal materials, with simple, solid and practical characteristics, simple and unadorned, suitable for cafes and bars and other places.
Second, according to the material classification
1. Wooden dining chair: Wooden dining chair is usually made of solid wood or artificial wood, with natural, environmental protection and warm characteristics, suitable for families and cafes and other places.
2. Metal dining chair: Metal dining chair is often made of metal materials such as iron, aluminum or stainless steel, with strong, durable and easy to clean characteristics, suitable for bars and cafes and other places.
3. Plastic dining chair: Plastic dining chair is usually made of polypropylene or polycarbonate and other plastic materials, with light, waterproof and easy to clean characteristics, suitable for fast food restaurants and school cafeterias and other places.
Third, according to the use of classification
Generally, it can be divided into two uses: domestic and commercial.
1. Home dining chair: Home dining chair pays attention to comfort and beauty, common dining table chair, folding chair and bar chair.
2. Commercial dining chairs: Commercial dining chairs pay attention to durability and practicality, common bar chairs, cafe chairs and fast food restaurant chairs.
In general: dining chair as one of the important furniture in restaurants, bars, cafes and other places, according to the design style, material and use of different, can be divided into a variety of categories. Choosing a dining chair that suits your place and needs can enhance the comfort and beauty of the dining environment.
Cafe chair,wholesale chair,stackable chair,connected chair
Foshan Shengshi Zhihui Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.sshotelfurniture.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)